Orbits and eyes anatomical illustrations eAnatomy

Fasciae of Orbit and Eyeball Anatomy Horizontal section, Medial palpebral ligament, Nasal cavity
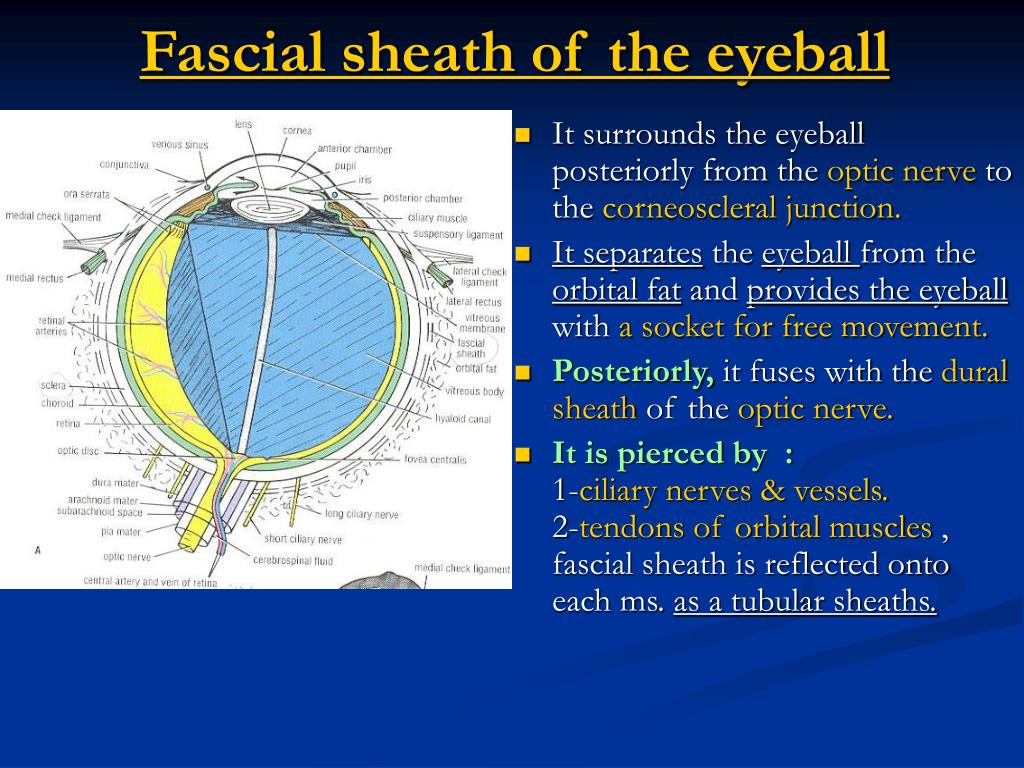
The fascial sheath of eyeball (Tenon's capsule; Fascia bulbi) is a thin membrane which envelops the bulb of the eye from the optic nerve to the ciliary region, separating it from the orbital fat and forming a socket in which it plays. Its inner surface is smooth, and is separated from the outer surface of the sclera by the periscleral lymph space.

Orbits and eyes anatomical illustrations eAnatomy
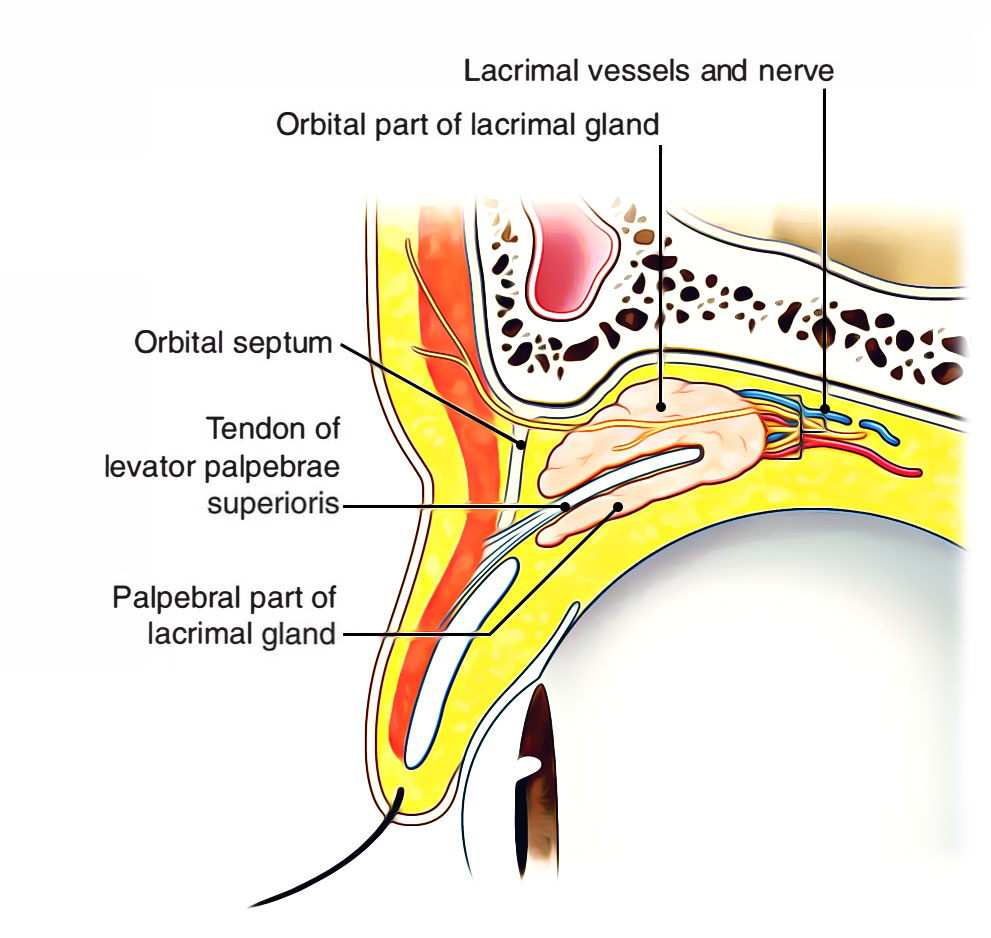
The inserting muscle fibers pierce the fascial sheath of the eyeball (Tenon's capsule), which in turn reflects back and creates a thin fascial sleeve around the muscle's tendon. This sleeve gives off an expansion called the medial check ligament that connects the medial rectus muscle with the medial wall of orbit.

How to perform a lateral canthotomy EyeGuru
Tenon's capsule ( / təˈnoʊn / ), also known as the Tenon capsule, fascial sheath of the eyeball ( Latin: vagina bulbi) or the fascia bulbi, is a thin membrane which envelops the eyeball from the optic nerve to the corneal limbus, separating it from the orbital fat and forming a socket in which it moves. The right eye in sagittal section.

Orbits and eyes anatomical illustrations eAnatomy
Tenon's capsule is a fascial sheath that encloses the eye, separating the sclera from the conjunctiva anteriorly and the orbital fat posteriorly. There is a potential space between Tenon's layer and the underlying sclera, although the two are firmly adherent to each other approximately 1.5 mm behind the limbus (the junction between sclera and cornea) and at the entry site of the optic.
Suspensory and Test Ligaments of the Eye Earth's Lab
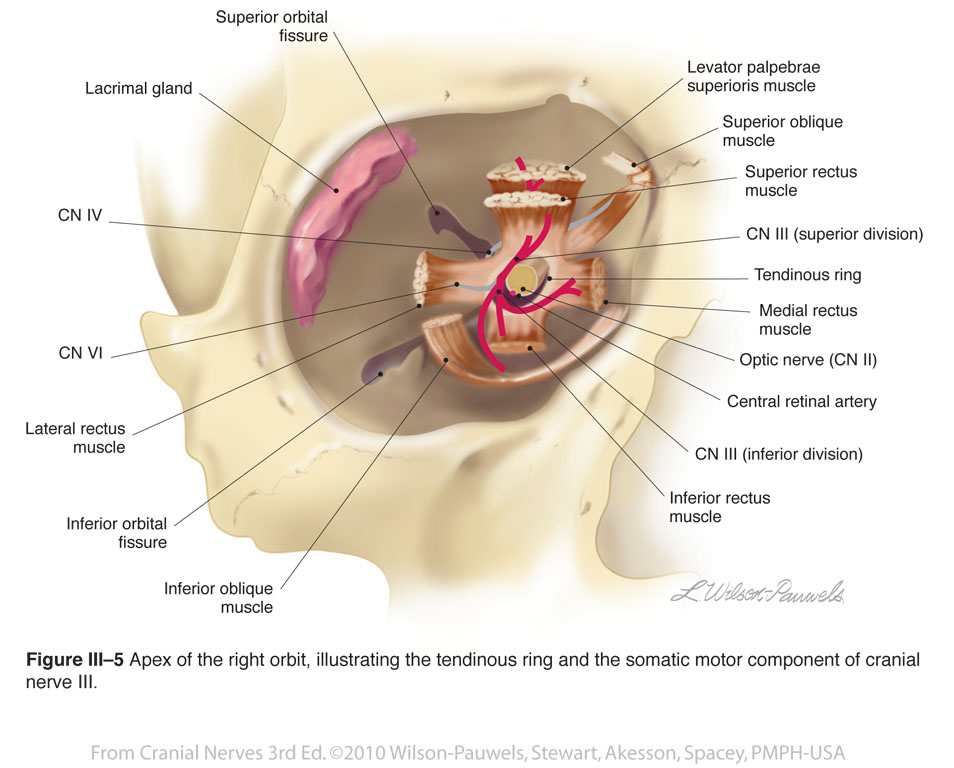
Fascial sheath of eyeball (Tenon) : Orbital cavity Extraocular muscles; Extrinsic muscles of eyeball Lacrimal apparatus : Orbital septum Eyeball/Eye : General Anatomy Lens (Eye) : Histology Iris : Anterior view Iridocorneal angle : Gonioscopy Corona ciliaris : Posterior view Retina : Histology

Choroid Function In Eye Map Of Body
Fascial Sheath of the Eyeball Connective Tissue Fascial Sheath of the Eyeball Vagina bulbi Structure Anatomical Relations Function List of Clinical Correlates Structure The fascial sheath of the eyeball surrounds the eye, extending from the optic nerve to the corneoscleral junction.

Fascial sheath of eye ball Tenon capsule capsule of Tenon Tenon's capsule YouTube
Awesome Prices & High Quality Here On Temu. New Users Enjoy Free Shipping & Free Return. Come and check All Categories at a surprisingly low price, you'd never want to miss it.

My journey around the world — FASCIAL ARTICULATIONS ⠀ [FASCIAL ANATOMY
Tenon's capsule ( / təˈnoʊn / ), also known as the Tenon capsule, fascial sheath of the eyeball ( Latin: vagina bulbi) or the fascia bulbi, is a thin membrane which envelops the eyeball from the optic nerve to the corneal limbus, separating it from the orbital fat and forming a socket in which it moves.

Orbit und Auge anatomische Abbildungen
Summary This chapter contains sections titled: Fascial Sheath of the Eyeball (Fascia Bulbi , Tenon's Capsule) The Eyeball Refractive Media of the Eye Clinical Problems Answers to Clinical Problems. Skip to Article Content; Skip to Article Information; Search within. Search term. Advanced.

Orbits and eyes anatomical illustrations eAnatomy
fas·ci·al sheath of eye·ball. A condensation of connective tissue on the outer aspect of the sclera from which it is separated by a narrow cleftlike episcleral space; the sheath is attached to the sclera near the sclerocorneal junction and blends with the fascia of the extraocular muscles. Synonym (s): Tenon capsule.
PPT Coats of the eyeball PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4368785
External to the sclera, the eyeball is enveloped by a thin fascial sheath (so-called Tenon's capsule) that extends from the optic nerve to the sclerocorneal junction (fig. 46-3). The sheath separates the globe from the orbital fat and acts as a socket in which the eye moves as in a ball-and-socket joint. It blends with the sheaths of the.

Órbitas e olhos ilustrações anatômicas
The posterior myofascial chain (PMC) or superficial back line encompasses a series of muscles interlinked by the deep fascia, extending from the foot to the fascial sheath of the eyeball. The deep cervical fascia of the neck, the epicranial aponeurosis of the head, and the fascial sheath of eyeball,.
The orbit Extraocular muscle annulus RANZCRPart1 Wiki Fandom
Describe the fascia of eyeball and orbit.What is Tenon's capsule?What is ligament of lockwood's?What is periorbita?Formation of check ligaments?location and.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/musculus-rectus-lateralis/FXZEHl1KYupJqsUh5hVew_M._rectus_lateralis_01.png)
Eyeball Structure and function Kenhub
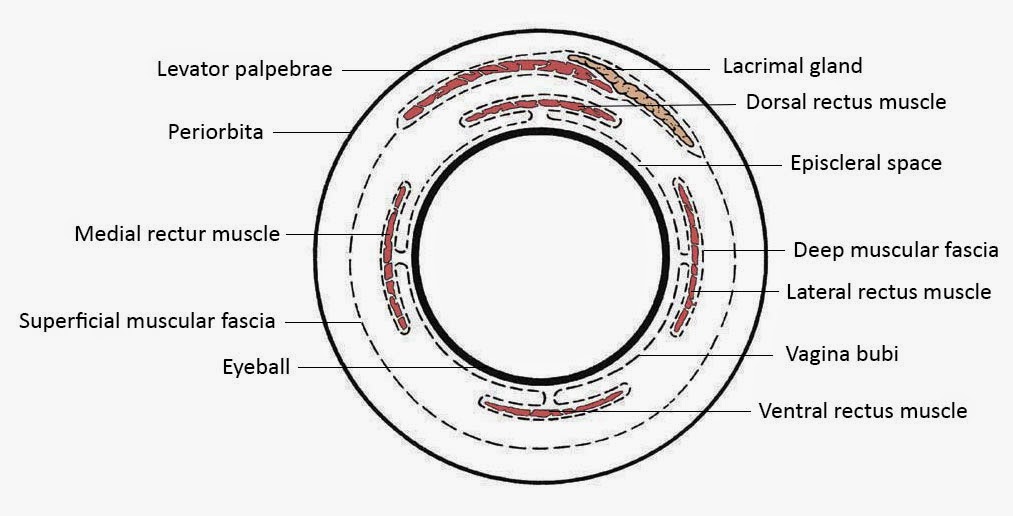
Overview Fascial sheath (Tenon's capsule) Function Fibrous layer Sclera Cornea Vascular layer (Uvea) Choroid Ciliary body Iris Nervous layer (Retina) Neural retina Retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) Blood supply Refractive media of the eyeball Lens Vitreous body Aqueous humor Clinical conditions

Microscopic findings of the upper eyelid. (A, B) Through the medial... Download Scientific Diagram
The eyes are responsible for detecting visible light, which ranges from 400 to 700 nanometers in wavelength. Objects can absorb and reflect different wavelengths of light. An object appears white if it reflects all wavelengths of light, and it appears black if it absorbs all wavelengths of light.
Eye Opener Anatomy Ocular Adnexa
The deep cervical fascia of the neck, the epicranial aponeurosis of the head, and the fascial sheath of eyeball, form the proximal PMC. Although the literature has reported an anatomical myofascial continuum between the neck, head, and eyes, the anatomical descriptions vary substantially.